0102030405
Self-Repairing Cars: A Glimpse into the Future of Automotive Technology
2024-06-20 10:26:14
Introduction
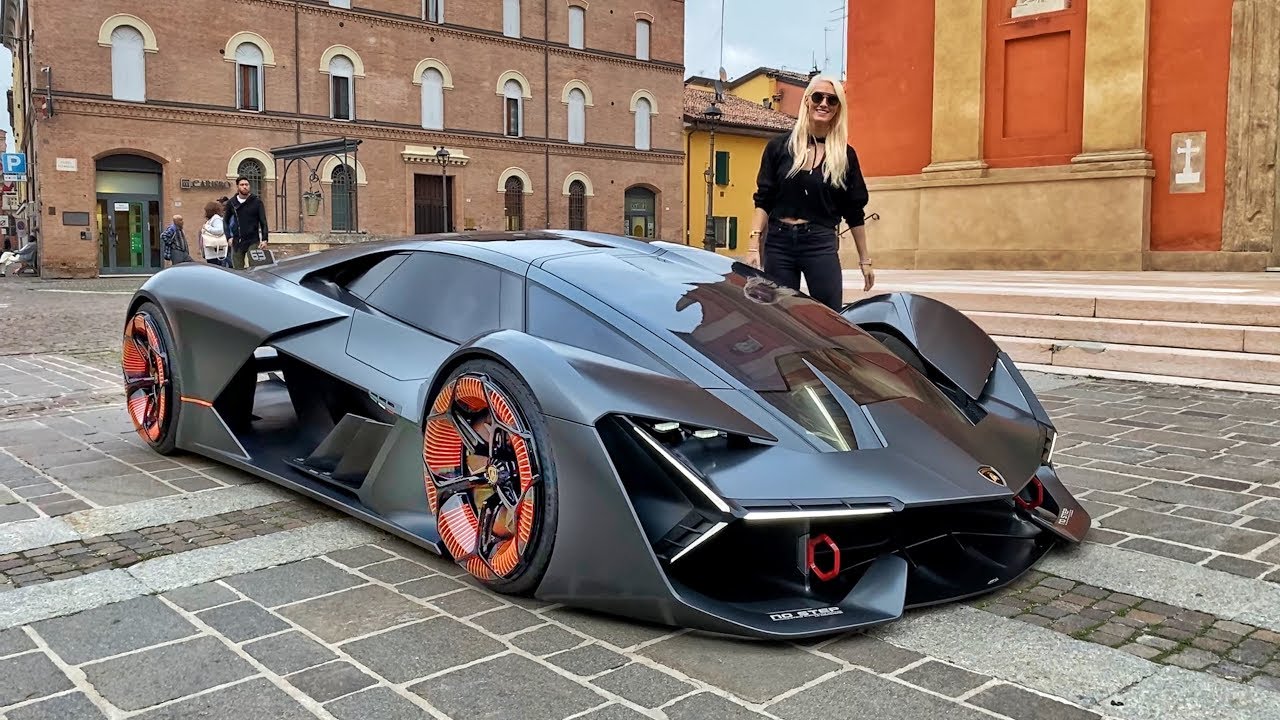
In a remarkable leap forward for automotive technology, the concept of self-repairing cars has transitioned from the realm of science fiction to a tangible reality. Imagine a vehicle capable of identifying and rectifying minor damages, scratches, and dents without the need for human intervention. This groundbreaking innovation promises to revolutionize the automotive industry, offering enhanced convenience, reduced maintenance costs, and prolonged vehicle lifespan. In this article, we explore the emerging trend of self-repairing cars and its implications for the future of transportation.
The Rise of Self-Repairing Technology
Self-repairing cars leverage a combination of advanced materials, artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics to detect and address damage in real-time. Inspired by the regenerative capabilities of living organisms, engineers have developed innovative solutions that enable vehicles to heal themselves automatically.
The key components of self-repairing technology include:
Smart Sensors: Embedded sensors throughout the vehicle continuously monitor its exterior for signs of damage, such as scratches, dents, or chipped paint.
Self-Healing Materials: The body panels and exterior surfaces of self-repairing cars are constructed from specialized materials that possess regenerative properties. These materials can repair minor damage by filling in scratches, smoothing out dents, or restoring paint finish.
AI Algorithms: AI algorithms analyze data collected by the sensors to identify the location, extent, and type of damage. Based on this analysis, the system determines the appropriate repair method and initiates the self-repair process.
Nanotechnology: Nanoparticles embedded within the self-healing materials facilitate rapid repair by reacting to external stimuli, such as temperature changes or pressure.
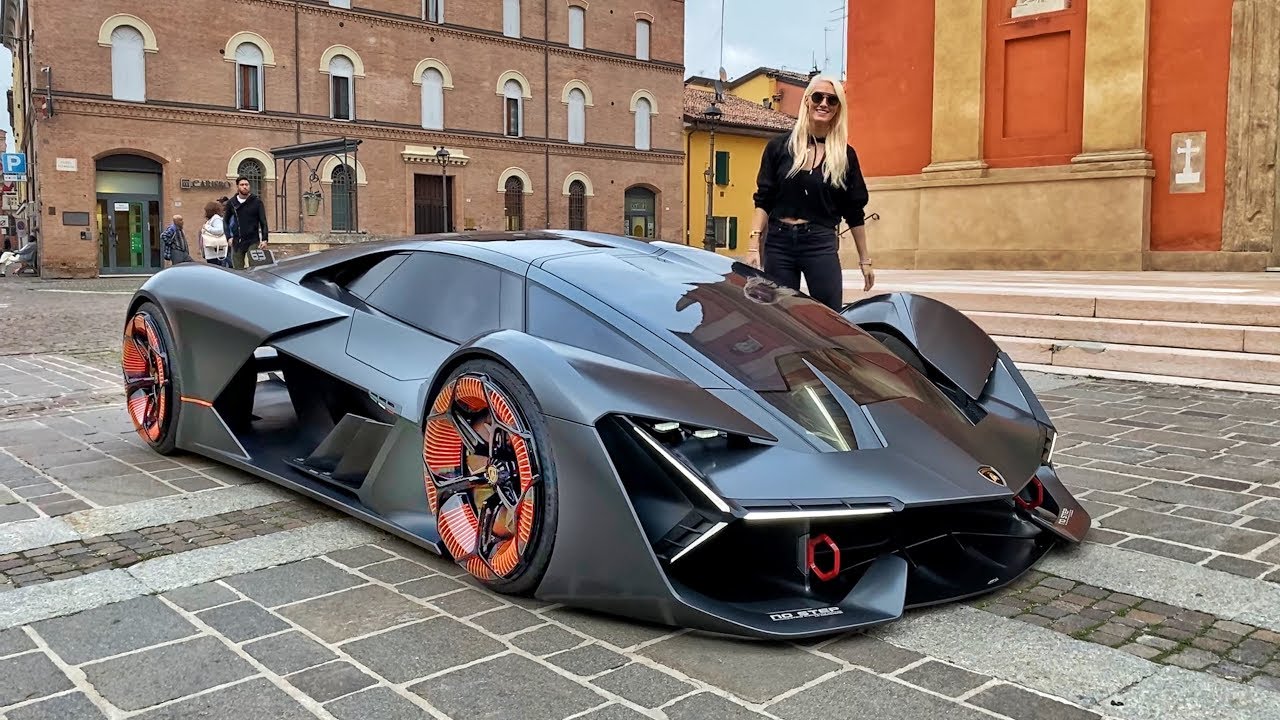

How Self-Repairing Cars Work
When a self-repairing car sustains minor damage, such as a scratch from a parking lot mishap or a small dent from a minor collision, the onboard sensors immediately detect the issue. The AI system analyzes the data and determines the optimal course of action.
If the damage is within the capabilities of the self-repairing technology, the system activates the self-healing materials. Nanoparticles within the damaged area are stimulated to fill in gaps, smooth out imperfections, and restore the surface to its original condition. This process occurs seamlessly and imperceptibly to the vehicle's occupants, preserving the aesthetics and integrity of the car.
For more significant damage that exceeds the capabilities of self-repairing technology, such as major collisions or structural issues, traditional repair methods may still be required. However, the ability of self-repairing cars to address minor damage autonomously significantly reduces the frequency and cost of conventional repairs.
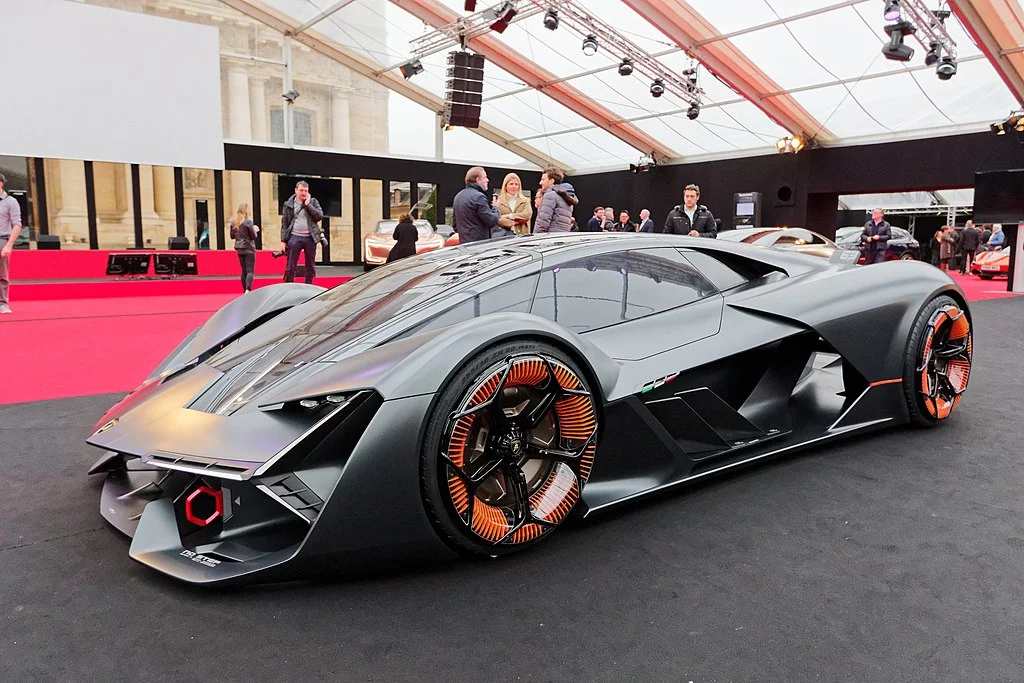

Implications for the Automotive Industry
The introduction of self-repairing cars has far-reaching implications for the automotive industry, reshaping the way vehicles are designed, manufactured, and maintained.
Enhanced Vehicle Longevity: Self-repairing technology extends the lifespan of vehicles by preventing minor damage from accumulating over time. As a result, cars remain in optimal condition for longer periods, reducing the need for premature replacement.
Reduced Maintenance Costs: With self-repairing cars, owners can expect lower maintenance costs associated with cosmetic repairs. The need for frequent visits to body shops or painting services diminishes, leading to significant cost savings over the vehicle's lifetime.
Improved Resale Value: Vehicles equipped with self-repairing technology are likely to retain higher resale values due to their superior condition and reduced wear and tear.
Safety and Convenience: Self-repairing cars contribute to enhanced safety on the road by addressing minor damage promptly, reducing the risk of corrosion and structural compromise. Additionally, owners enjoy the convenience of a vehicle that maintains its appearance and functionality with minimal effort.
Challenges and Considerations
While the concept of self-repairing cars holds immense promise, several challenges and considerations must be addressed before widespread adoption:
Complexity of Technology: Developing self-repairing technology that is reliable, cost-effective, and scalable presents significant engineering challenges.
Environmental Impact: The production and disposal of self-repairing materials may have environmental implications, necessitating careful consideration of sustainability measures.
Regulatory Approval: Self-repairing cars must meet stringent safety and regulatory standards before they can be commercialized and deployed on public roads.
Consumer Acceptance: Consumer acceptance and adoption of self-repairing technology may vary, depending on factors such as cost, reliability, and perceived value.
Conclusion
Self-repairing cars represent a paradigm shift in automotive technology, offering a glimpse into a future where vehicles are capable of autonomous maintenance and repair. While still in the early stages of development, the potential benefits of self-repairing technology are undeniable, promising enhanced convenience, reduced costs, and improved vehicle longevity.
As engineers and researchers continue to refine self-repairing technology and address existing challenges, the day when self-repairing cars become a common sight on the road draws closer. In the meantime, the automotive industry remains at the forefront of innovation, driving progress towards a future where cars not only transport us but also take care of themselves.