0102030405
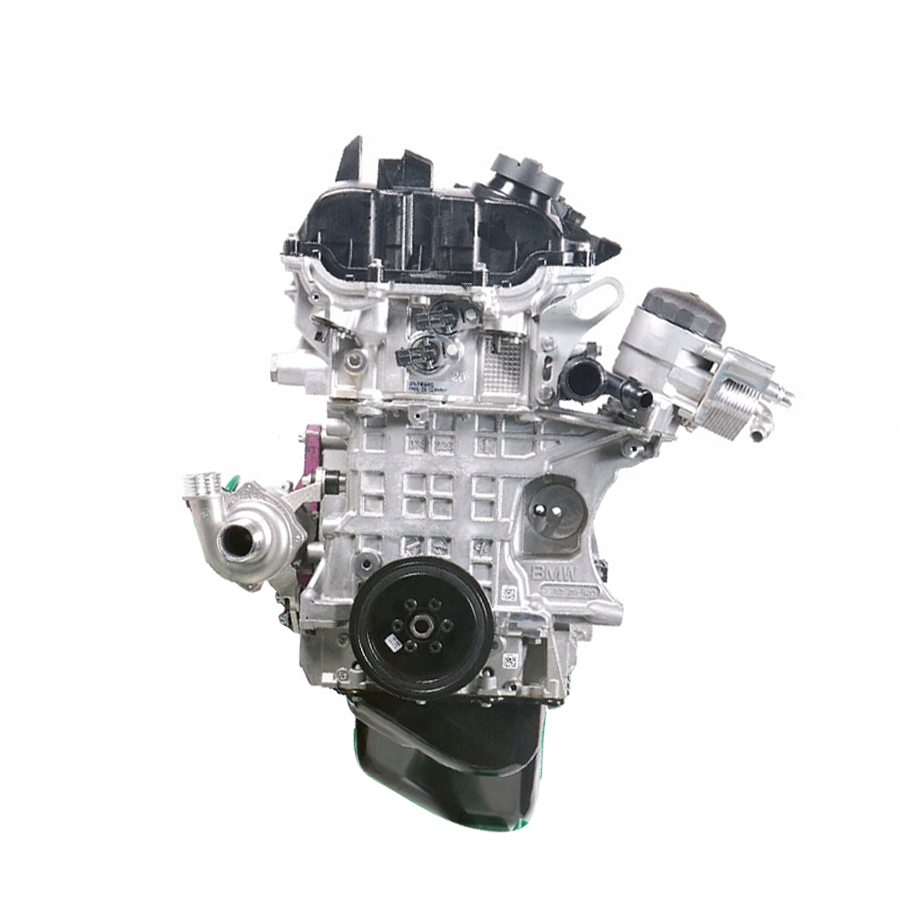
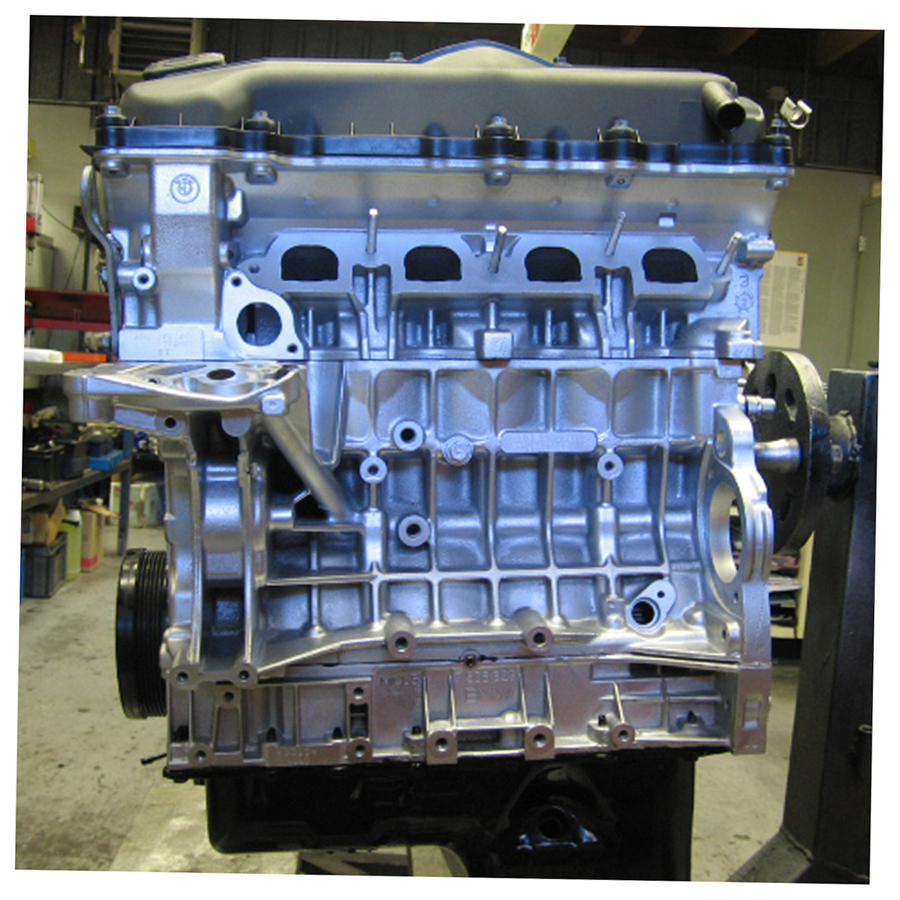
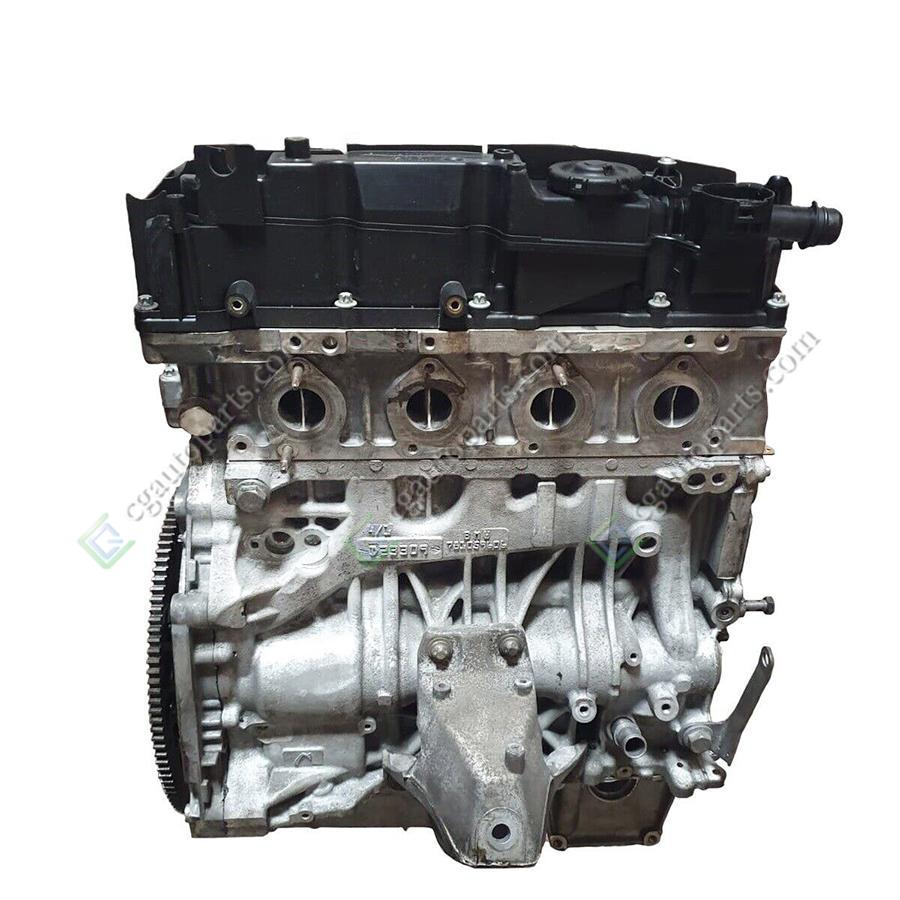
COMPLETE ENGINE : Engine Mitsubishi 4D56
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
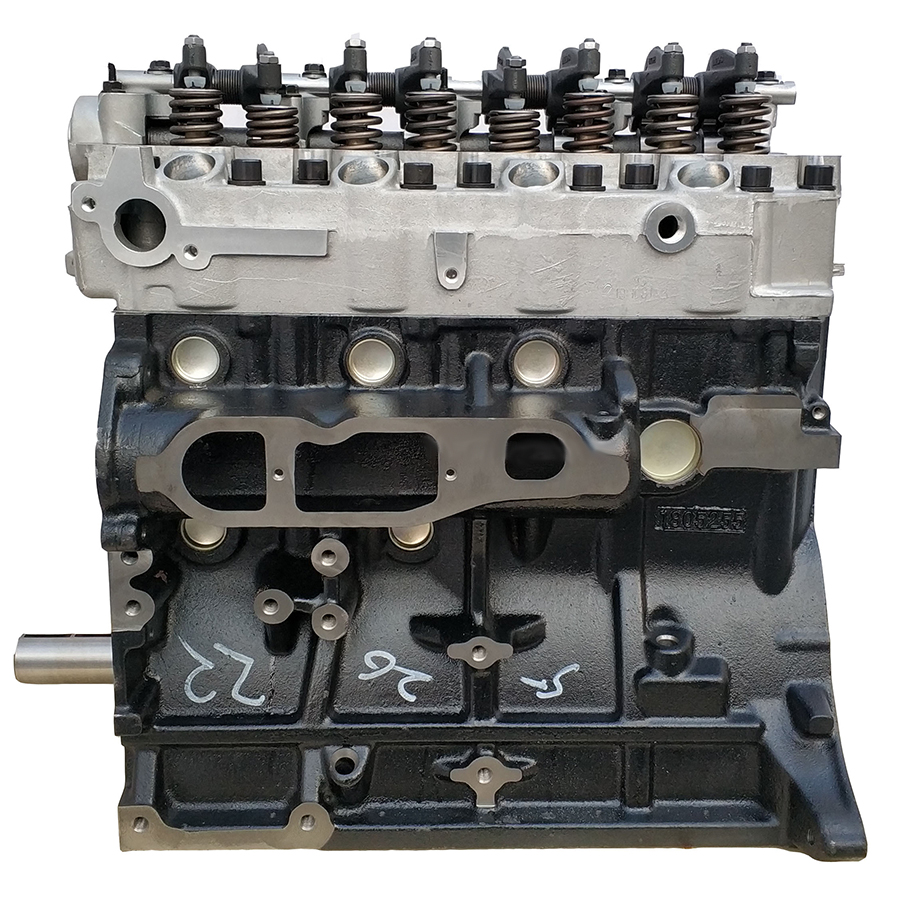





The 2.5-liter Mitsubishi 4D56 diesel engine was assembled by the concern from 1986 to 2016 and was installed on Pajero and Pajero Sport SUVs, L200 pickups and Delica minibuses. This power unit served as the basis for the well-known Hyundai D4BA, D4BF and D4BH diesel engines.
The 4D56 engine was developed in 1986 by the Japanese automobile company Mitsubishi. After that, for 10 years, Japanese engineers were finalizing it. The main task for the designers was to increase the power and service life, to ensure normal maintainability.
4D56 is designed according to the standard layout, the cylinder heads are made of aluminum and the block is made of cast iron. It was the use of such alloys that made it possible to achieve the smallest mass and provide excellent thermal stability. In 2001, the production of 4D56 with a Common Rail fuel system began. New pistons were used, which reduced the compression ratio to 17. All this allowed to increase power and torque.
The 4D5 family also includes engines: 4D55.


The engine was installed on:
Mitsubishi Delica 3 (P03) in 1986 – 1999; Delica 4 (PA4) in 1994 – 2007;
Mitsubishi L200 2 (K10) in 1986 – 1996; L200 3 (K70) in 1996 – 2006; L200 4 (KB) in 2006 – 2016;
Mitsubishi Pajero 1 (L040) in 1986 – 1991; Pajero 2 (V30) in 1990 – 2000; Pajero 3 (V70) in 1999 – 2006;
Mitsubishi Pajero Sport 1 (K90) in 1996 – 2008; Pajero Sport 2 (KH) in 2008 – 2016.
Specifications
Manufacturer |
Kyoto engine plant |
Production years |
1986-2016 |
Displacement, cc |
2477 |
Fuel system |
vortex chamber |
Power output, hp |
74/4200 |
Torque output, Nm |
142/2500 |
Cylinder block |
cast iron R4 |
Block head |
aluminum 8v / 16v |
Cylinder bore, mm |
91.1 |
Piston stroke, mm |
95 |
Compression ratio |
21.0 |
Features |
no |
Hydraulic lifters |
no |
Timing drive |
belt |
Turbocharging |
no |
Recommended engine oil |
5W-30, 5W-40 |
Engine oil capacity, liter |
6.5 |
Fuel type |
diesel |
Euro standards |
Euro 2 |
Fuel consumption, L/100 km (for Mitsubishi Pajero Sport 2004) |
12.6 |
Engine lifespan, km |
~400 000 |
Weight, kg |
193 |
Modifications 4D56
Non-Turbo:
Power – 74 hp (55 kW) at 4200 rpm;
Torque – 142 Nm @ 2500 rpm;
Engine type – in-line, 4-cylinder SOHC;
The Compression ratio is 21.0: 1.
Non-intercooled Turbo:
Power – 84 HP (62 kW) at 4200 rpm;
Torque – 201 Nm @ 2000 rpm;
Engine type – in-line, 4-cylinder SOHC.
Intercooled Turbo (TD04 Turbo):
Power – 90 HP (67 kW) at 4200 rpm;
Torque – 197 Nm @ 2000 rpm;
Engine type – in-line, 4-cylinder SOHC;
The Compression ratio is 21.0: 1.
Intercooled Turbo (TD04 water-cooled Turbo)*:
Power – 99 HP (74 kW) at 4300 rpm;
Torque – 240 Nm @ 2000 rpm;
Engine type – in-line, 4-cylinder SOHC;
The Compression ratio is 21.0: 1.
*Also known as Hyundai D4BH.
Intercooled Turbo TF035HL2 (1st Generation DI-D):
Power – 114 hp (84 kW) at 4000 rpm;
Torque – 247 Nm @ 2000 rpm;
Engine type – in-line, 4-cylinder;
The Compression ratio is 17.0: 1.
Intercooled Turbo (2nd Gen DI-D):
Power – 136 HP (100 kW) at 4000 rpm;
Torque – 320 Nm @ 2000 rpm;
Engine type – in-line, 4-cylinder;
The Compression ratio is 17.0: 1.
Intercooled Turbo (3rd Gen with DI-D variable geometry turbine)
With manual transmission:
Power – 178 hp (131 kW) at 4000 rpm;
Torque – 400 Nm @ 2000 rpm;
Engine type – in-line, 4-cylinder;
Compression ratio – 16.5: 1.
With automatic transmission:
Power – 178 hp (131 kW) at 4000 rpm;
Torque – 350 Nm @ 1800 rpm;
Engine type – in-line, 4-cylinder;
Compression ratio – 16.5: 1.
Disadvantages of the Mitsubishi 4D56 engine
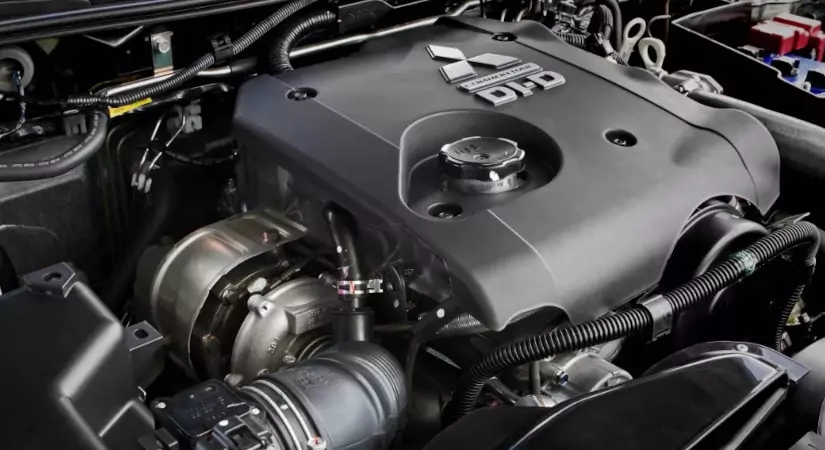

This diesel unit is afraid of overheating and the cylinder head gasket breaks regularly. But replacing the gasket is not enough, you will have to grind the mating surfaces. After a couple of breakdowns, cracks can often be found near valves or prechambers.
Another serious problem of this engine is the breakdown of the crankshaft, and this happens especially often during prolonged movement at low engine speeds. In engines with a Common Rail system, the crankshaft journals are thicker and breakdown is less common.
For obvious reasons, the fuel system delivers the bulk of the trouble to the owners of such diesel engines, and this applies to both vortex chamber and Common Rail versions.
The timing belt does not have a large resource and does not always run the required 90,000 km, especially if you do not tighten it every 30,000 km. With a break, it only breaks off the rocker, but in the Common Rail version of the engine, it often pulls out the mounting bolts of the camshaft yokes. When a balancer belt breaks, it usually falls under the timing belt and also breaks it.
Also, oil leaks are common here, almost all gaskets and seals sweat, the crankshaft pulley and the vacuum pump have a low resource, the EGR valve clogs, a lot of trouble is associated with airing, and pistons burst at the slightest tuning. And do not forget to check the valve clearance every 20,000 km or they will simply burn out.